El Niño Effects, Flattening Production and ISO Summer Readiness
3 min readDuring the June Energy Market Intel Webinar, Constellation’s Commodities Management Group (CMG) presented on the outlook for summer weather, natural gas production and storage levels and regional electricity updates.
Market analysts opened the webinar with a look at the short-term weather forecast characterized by a cooler-than-normal start to summer across the country.
Weather Update
Constellation’s chief meteorologist analyzed the forecast for the summer season, which begins June 21 – summer solstice. He mentions that the first three weeks of June have been largely cooler than normal in key electric power markets, particularly in the Midwest and much of the Mid-Atlantic. A lot of rain and a stormy pattern has prevailed so far, keeping temperatures at bay in many regions.
Some meaningful heat is still possible, if not likely, in the Midwest into the East and Northeast with an emphasis on the second half of summer.
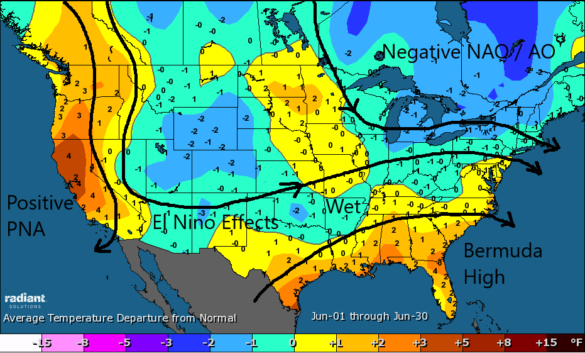
Source: Radiant Solutions
Flattening Gas Production & Improvement in Storage Numbers
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), natural gas production has increased on a year-over-year basis — about +/-10%. This has largely been the key factor in keeping gas prices in check and pressured to the downside through the second quarter. However, natural gas production has been flat through the first half of the year, contrary to expectations.
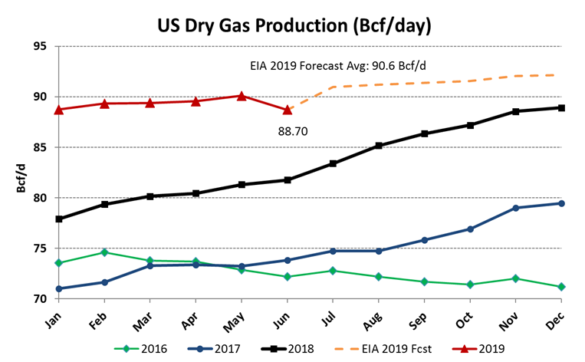
Source: Energy Information Administration
Natural gas injections into storage have made several records in the second quarter erasing the year-over-year deficit, averaging 95.8 Bcf/week for the 10 weeks since April 1st. Inventories remain below the five-year average, but with a slow start to summer and lagging air conditioning load, it is more than likely that inventories will meet the five-year average by the end of October.
A much more bearish storage picture coupled with the lack of strong heat to this point has kept power and gas prices under pressure.
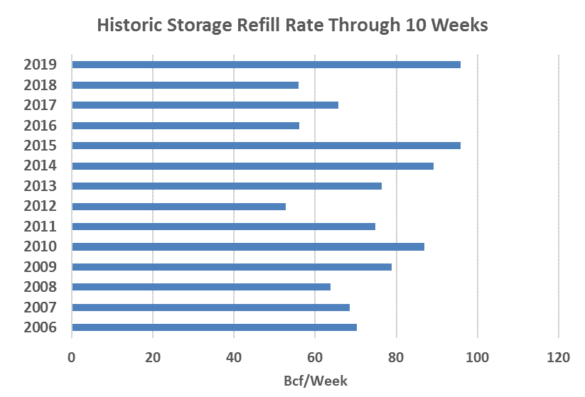
Source: Energy Information Administration
The Latest in Power Markets
Constellation’s CMG team broke down the findings from the North American’s Electric Reliability Commission (NERC’s) Summer Reliability Assessment and identified the key risks in CAISO and ERCOT. NERC noted all regions have adequate generation reserves except ERCOT at 8.6% versus 13.75%. In ERCOT, load continues to grow at +2% annually, and most of the new generation is comprised of renewables that will need to be supported by gas-fired generation, which is seeing limited new builds.
In addition, NERC did identify the ongoing need in CAISO for gas plants to rely on gas storage for summer reliability.
To stay updated on these topics and more, join us in May for our next Energy Market Intel Webinar on July 17, 2019, at 2:00 p.m. ET. In next month’s webinar, we will look at how summer 2019 is comparing to a year ago and what current trends imply for August forecasts. We will continue to monitor Lower 48 production and natural gas demand factors on a year-over-year basis as well as explore any index volatility in power markets.
